Geodynamic code development
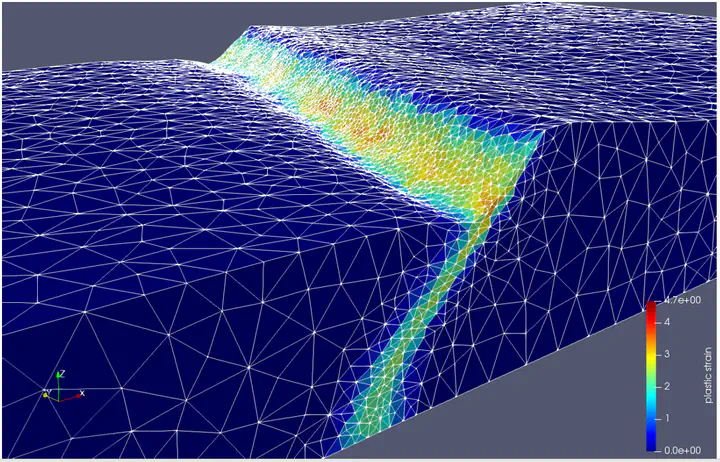 Three-dimensional model for core complex formation created with DES3D. Accelerated on NVidia V100 graphics card.
Three-dimensional model for core complex formation created with DES3D. Accelerated on NVidia V100 graphics card.The main goal of this project is to improve DES3D (Dynamic Earth Solver in 3D), an open-source geodynamic modeling code. in terms of the types of physical processes it can model and the speed
Performance
DynEarthSol (DES) is multithread-parallel through OpenMP. The parallel performance scales well up to 16 threads on recent multi-core CPUs and will be tested on newer CPUs models whenever possible.
DES has been enabled to run on NVIDIA GPUs through CUDA and then on other hardware through OpenACC. The overall parallelization is illustrated in the figure below.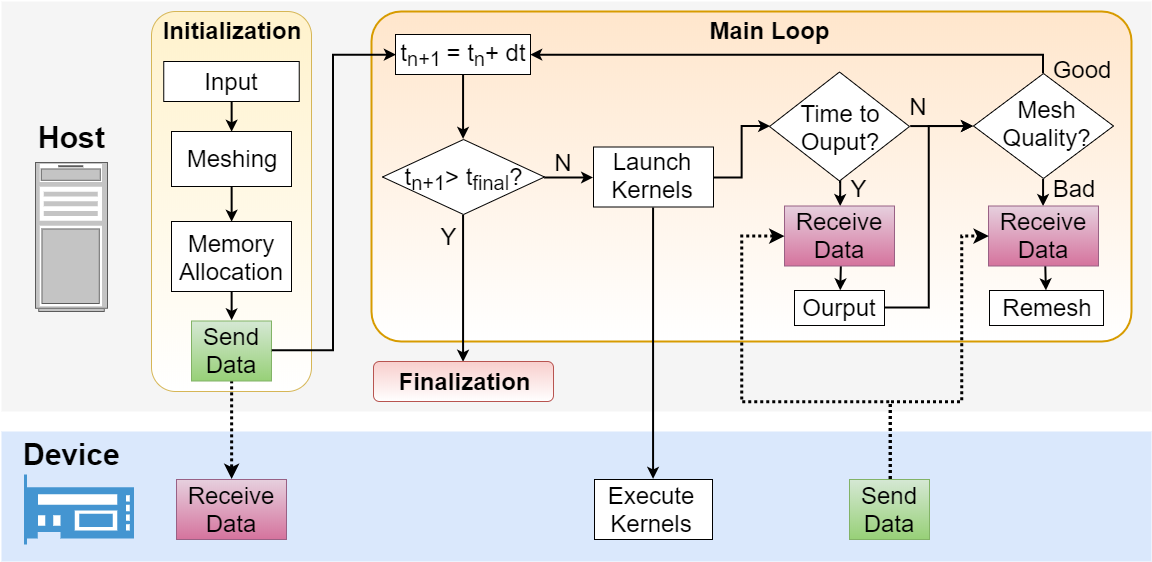
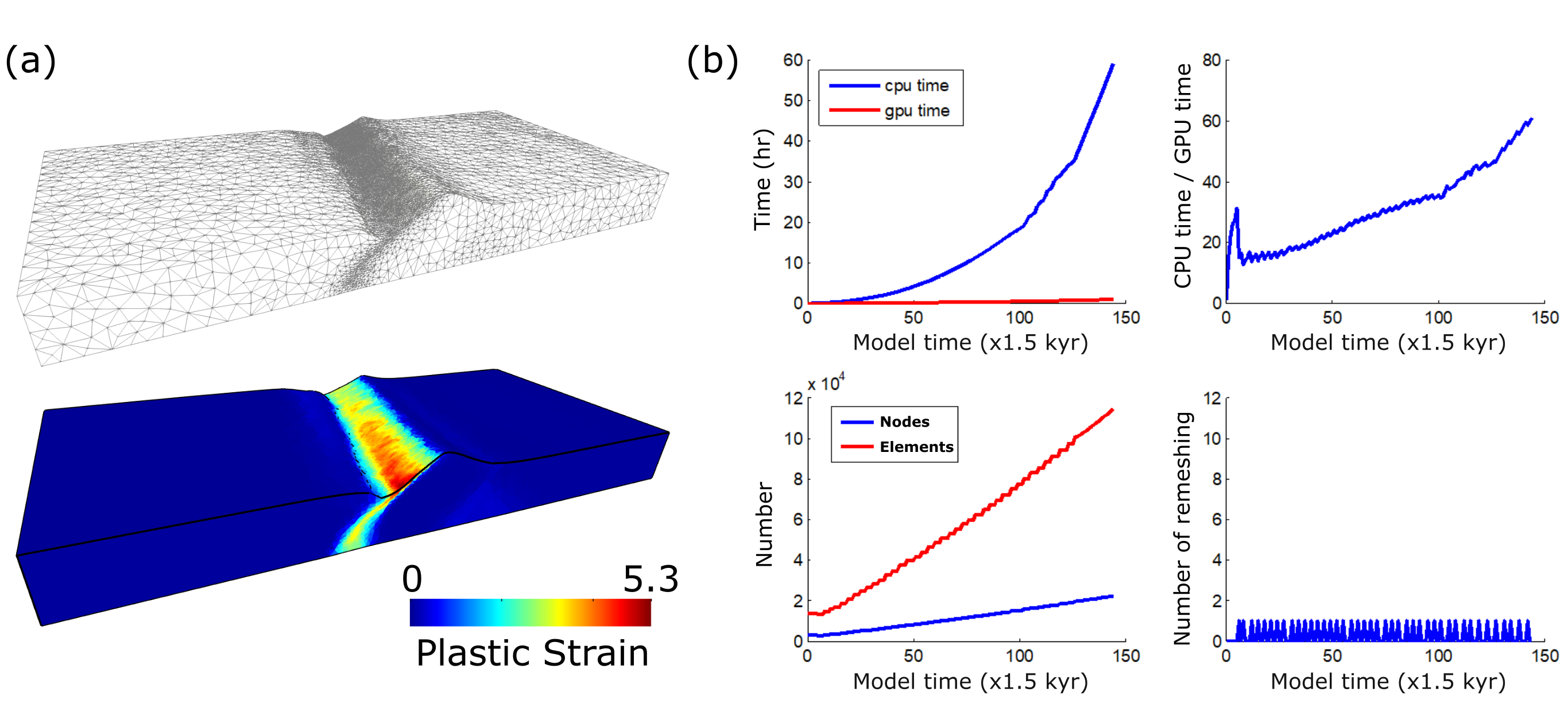
Functionality
In additional to its core function to simulate large deformation in temperature-dependent elasto-visco-plastic material, we are adding other useful capabilities:
- Rate-and-state friction law by Tong and Lavier (Nature Comm., 2018). With this new friction law, we can better model an entire earthquake cycle as well as the consequences of its numerous repetition.
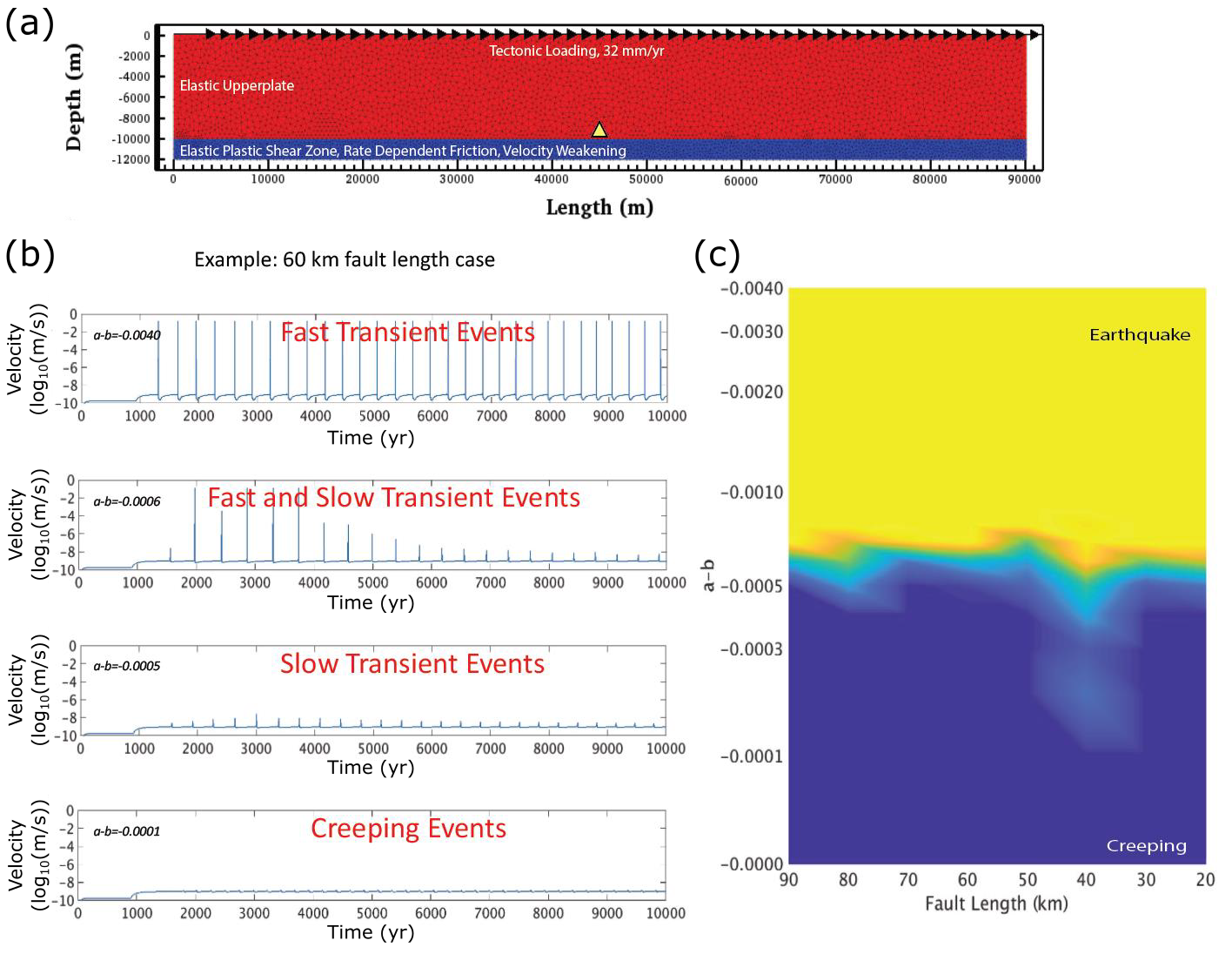
Earthquake cycles modeled with a rate-and-friction law implemented in DES3D - Pseudo-transient method, an efficient extension of Cundall’s damping scheme for dynamic relaxation
- Structured meshing that will complement the default unstructured meshing with P1 elements and provide convenience in some types of models
- Laghost: Migration of code base to MFEM. MFEM is an arbitrary-order finite element library for extreme-scale parallel computation. Laghost is an effort to build DES’s main algorithm on MFEM.